Emotional Design in UX: Strategies to Boost Engagement and Build Brand Loyalty
Rohan Roy
Dec 27, 2024
UI/UX






Emotional design goes beyond aesthetics and makes digital products valuable and meaningful to users. It achieves this by exploiting human emotions to make ordinary interactions extraordinary experiences, leading to increased engagement and loyalty. This approach is about creating interfaces that are not only pretty to look at but also make us feel safe, that we can trust, and that they’re exciting. Let’s explore how emotional design fuels engagement and how brands get noticed in this day and age of user-driven design.
The Role of Emotional Design in Building Meaningful User Experiences
Emotional design is creating digital products and experiences that connect emotionally with users. It goes beyond functionality to discover connections that make users feel understood, valued, and engaged. Emotional design makes interactions emotional with visual aesthetics, interactive elements, and psychology. Consequently, it plays a vital role in user experience (UX) as it closes the gap between user expectations and brand identity, and all interactions should feel intuitive and enjoyable.
Products that trigger emotions—such as joy, surprise, or trust—involve users and make it possible to engrave products in memory. Emotional design is a means to ensure that a user uses a product and not just the product, enabling him to stick to it and thus increase his probability of coming back. Not only would this increase usability, but it would also increase user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Connection Between Emotions and User Perception
How people feel about products is critical to interacting with and perceiving them. What users think when seeing a good app or website is often dictated by the emotional responses they get. A positive set of emotions distinguishes a good interface with the advantage of teaching users how to use it without much effort. On the other hand, a poorly designed interface can cause frustration in users, which will make them decide to abandon the product.
Cognitive psychology reveals that emotions drive decision-making. Users trust products that make them feel good, even if they do not feel good. Strategically fusing emotional design allows brands to influence users' behavior and perceptions to make their products a more attractive choice in the market.
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Don Norman, a pioneer in UX design, identified three levels of emotional design that contribute to the user experience: Behavioral, visceral, and reflective.
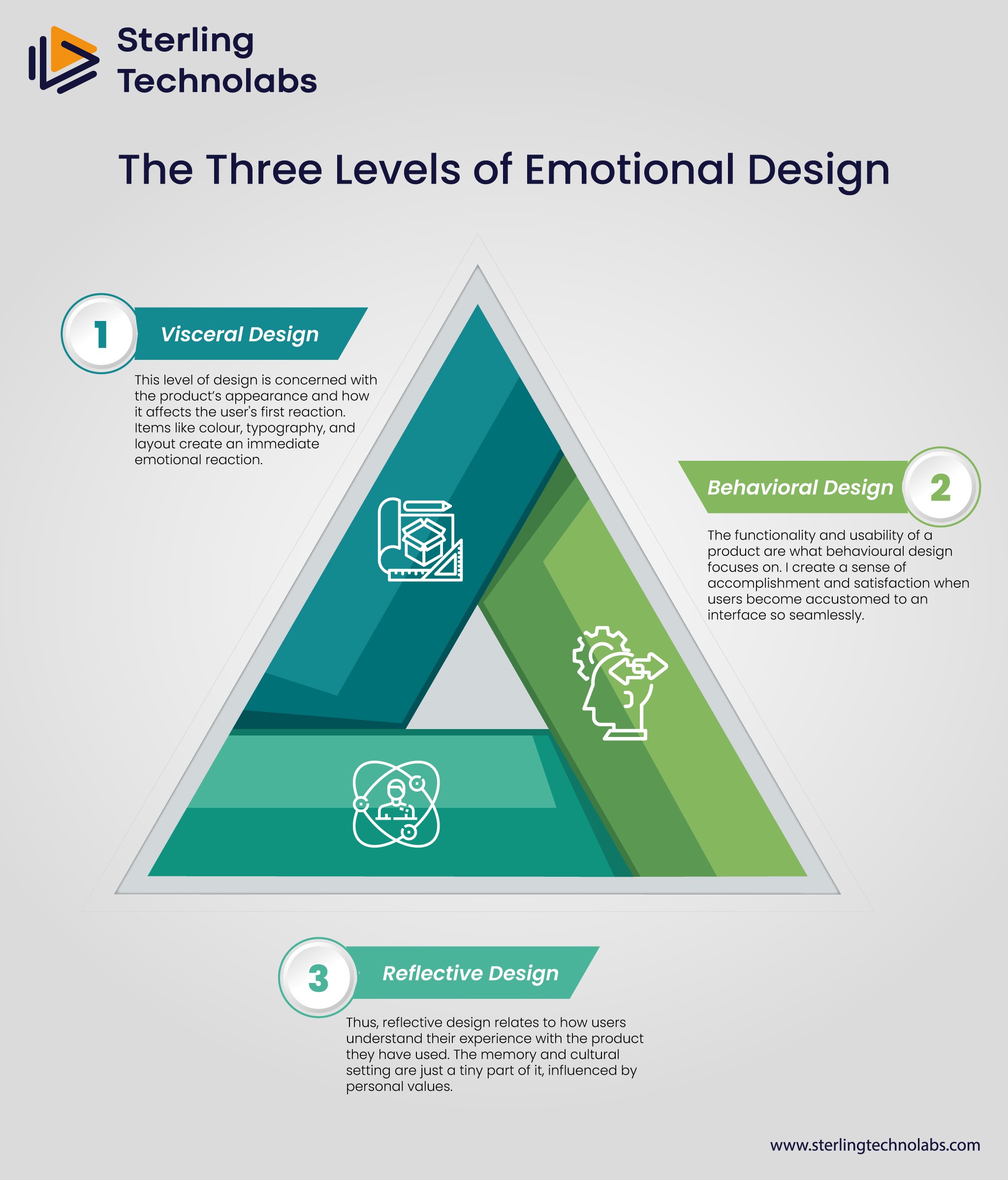
Visceral Design
This level of design is concerned with the product’s appearance and how it affects the user's first reaction. Items like color, typography, and layout create an immediate emotional reaction. For one, Apple's sleek product designs, which create a feeling of luxury and sophistication, help set a positive tone early on in the user experience.
Behavioral Design
The functionality and usability of a product are what behavioral design focuses on. I create a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when users become accustomed to an interface so seamlessly. Behavioral design — making booking a process other than checkout — is what brands like Airbnb have mastered.
Reflective Design
Thus, reflective design relates to how users understand their experience with the product they have used. The memory and cultural setting are just a tiny part of it, influenced by personal values. Take, for example, Nike's "Just Do It" campaigns, which resonate on a self-reflective level, encourage users, and help align with what the users wish to achieve.
Emotional design attains holistic and meaningful user experiences by engaging it at all three levels.
Why Emotional Design Is Critical for User Engagement
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, organization often refers to emotional design. Strong products that evoke strong emotional connections will stand out and lead users to engage with and advocate for the brand. Effective emotional design builds trust, promotes discovery, connects, and provides a sense of belonging, which is necessary for sustained engagement.
Additionally, emotional design plays into the basic human desire to connect. Emotional design allows brands to achieve this through interactive messages, empathetic messaging, and even personalized interactions through playful animations. Emotional resonance translates to higher retention rates and greater brand loyalty because products that provoke emotions have more likelihood of users coming back.
Emotions and Their Influence on Decision-Making and Loyalty
Decision-making is centered on emotions. According to neuroscience studies, when users decide to interact with a product, emotional responses usually trump rational thought. A good example is if you have a well-crafted onboarding process that promotes curiosity or fun, people will follow through, whereas a frustrating experience will make them abandon it.
Similar to emotions, emotions influence loyalty. Users are more likely to stay with a brand if they build a positive emotional connection to said brand. To make you feel understood and appreciated, companies like Spotify and Netflix have been excelling with emotional design to provide personal experiences to users.
Examples of Brands Successfully Leveraging Emotional Design
Notable brands such as Apple, Airbnb, and Duolingo have proven the power of emotional design in creating empathetic and memorable user experiences.
Apple: Apple’s minimalist design philosophy evokes elegance and exclusivity. The battlespace that Apple has engineered, starting with the iPhone and extending to the MacBook, is seamless, and its product ecosystems deliver convenience and delight at every touchpoint.
Airbnb: Airbnb’s design promotes a feeling of adventure and belonging. Their software is also intuitive, accompanied by emotionally resonant imagery and personalized recommendations that make users feel valued travelers rather than customers.
Duolingo: The language learning app combines playful animations, gamification, and positive messages in learning. Duolingo convinces users that a difficult task is fun rather than the reverse.
Principles of Emotional Design
There are some key principles to implementing emotional design to get user engagement right. One is overwhelming empathy, as you must understand the user’s needs, preferences, and the points where they struggle most to create solutions that make the most sense personally. Equally, aesthetics are important because visually appealing designs can generate positive emotions and make you leave a strong first impression.
Consistency is the key to ensuring your brand experience is consistent; the brand experiences for all the touch points build trust and familiarity with your brand. The interactive elements help add value by incorporating playfulness and intrigue into the user's engagement. Personalization lets users feel valued and understood, enabling you to personalize the user's experience. Combining these principles forms a robust and powerful framework around emotional design.
Best Practices for Implementing Emotional Design
To apply emotional design for effect, UX and UI designers must take a user-centric approach based on strategy and empathy. The only thing that matters is to reach the audience, and you need to put in ample work to understand them and conduct research to know what emotional triggers or preferences would work for them. There are also tactics like leveraging color psychology since colors can make people feel certain things. For example, we could pick blue to invoke trust or yellow for optimism.
Playful animations and congratulatory messages that embed micro-interactions like these help break up the flow and make the experience a bit merrier. Storytelling also matters, allowing brands to link their stories with their owners’ stories, values, and dreams of belonging.
Conclusion
Emotional design is an excellent means to tune purchaser engagement, brand loyalty, and customer retention. Brands can lead a visceral, behavioral, or reflective experience with user emotional needs that resonate profoundly and leave an impression. We know from companies like Apple and Airbnb that emotional design is an investment in boosting user satisfaction that pays off over the long term.
Emotional design is a way to make yourself seen and connected with the user on a human level in a world of fierce competition. Businesses can build digital experiences that arouse and retain their audiences by prioritizing empathy, aesthetics, and personalization.

FAQs
Q: What is emotional design, and why is it important in user experience?
A: Emotional design aims to create more positive digital products, increasing users' emotional appeal and satisfaction with their usage.
Q: How does emotional design influence user engagement?
A: Emotional design improves trust, promotes exploration, and enhances memories of your experiences to improve user engagement.
Q: What are the key principles of emotional design?
A: The most crucial emotional design principles are empathy, aesthetics, consistency, interactivity, and personalization.
Q: Can emotional design improve customer retention?
A: Emotional design enables us to create positive emotional connections that help increase user loyalty and retention.
Q: How does color psychology contribute to emotional design?
A: Specific colors invoke specific emotions, which affect how users perceive and interact with that product. For instance, blue represents trust, and red represents excitement.
Emotional design goes beyond aesthetics and makes digital products valuable and meaningful to users. It achieves this by exploiting human emotions to make ordinary interactions extraordinary experiences, leading to increased engagement and loyalty. This approach is about creating interfaces that are not only pretty to look at but also make us feel safe, that we can trust, and that they’re exciting. Let’s explore how emotional design fuels engagement and how brands get noticed in this day and age of user-driven design.
The Role of Emotional Design in Building Meaningful User Experiences
Emotional design is creating digital products and experiences that connect emotionally with users. It goes beyond functionality to discover connections that make users feel understood, valued, and engaged. Emotional design makes interactions emotional with visual aesthetics, interactive elements, and psychology. Consequently, it plays a vital role in user experience (UX) as it closes the gap between user expectations and brand identity, and all interactions should feel intuitive and enjoyable.
Products that trigger emotions—such as joy, surprise, or trust—involve users and make it possible to engrave products in memory. Emotional design is a means to ensure that a user uses a product and not just the product, enabling him to stick to it and thus increase his probability of coming back. Not only would this increase usability, but it would also increase user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Connection Between Emotions and User Perception
How people feel about products is critical to interacting with and perceiving them. What users think when seeing a good app or website is often dictated by the emotional responses they get. A positive set of emotions distinguishes a good interface with the advantage of teaching users how to use it without much effort. On the other hand, a poorly designed interface can cause frustration in users, which will make them decide to abandon the product.
Cognitive psychology reveals that emotions drive decision-making. Users trust products that make them feel good, even if they do not feel good. Strategically fusing emotional design allows brands to influence users' behavior and perceptions to make their products a more attractive choice in the market.
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Don Norman, a pioneer in UX design, identified three levels of emotional design that contribute to the user experience: Behavioral, visceral, and reflective.

Visceral Design
This level of design is concerned with the product’s appearance and how it affects the user's first reaction. Items like color, typography, and layout create an immediate emotional reaction. For one, Apple's sleek product designs, which create a feeling of luxury and sophistication, help set a positive tone early on in the user experience.
Behavioral Design
The functionality and usability of a product are what behavioral design focuses on. I create a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when users become accustomed to an interface so seamlessly. Behavioral design — making booking a process other than checkout — is what brands like Airbnb have mastered.
Reflective Design
Thus, reflective design relates to how users understand their experience with the product they have used. The memory and cultural setting are just a tiny part of it, influenced by personal values. Take, for example, Nike's "Just Do It" campaigns, which resonate on a self-reflective level, encourage users, and help align with what the users wish to achieve.
Emotional design attains holistic and meaningful user experiences by engaging it at all three levels.
Why Emotional Design Is Critical for User Engagement
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, organization often refers to emotional design. Strong products that evoke strong emotional connections will stand out and lead users to engage with and advocate for the brand. Effective emotional design builds trust, promotes discovery, connects, and provides a sense of belonging, which is necessary for sustained engagement.
Additionally, emotional design plays into the basic human desire to connect. Emotional design allows brands to achieve this through interactive messages, empathetic messaging, and even personalized interactions through playful animations. Emotional resonance translates to higher retention rates and greater brand loyalty because products that provoke emotions have more likelihood of users coming back.
Emotions and Their Influence on Decision-Making and Loyalty
Decision-making is centered on emotions. According to neuroscience studies, when users decide to interact with a product, emotional responses usually trump rational thought. A good example is if you have a well-crafted onboarding process that promotes curiosity or fun, people will follow through, whereas a frustrating experience will make them abandon it.
Similar to emotions, emotions influence loyalty. Users are more likely to stay with a brand if they build a positive emotional connection to said brand. To make you feel understood and appreciated, companies like Spotify and Netflix have been excelling with emotional design to provide personal experiences to users.
Examples of Brands Successfully Leveraging Emotional Design
Notable brands such as Apple, Airbnb, and Duolingo have proven the power of emotional design in creating empathetic and memorable user experiences.
Apple: Apple’s minimalist design philosophy evokes elegance and exclusivity. The battlespace that Apple has engineered, starting with the iPhone and extending to the MacBook, is seamless, and its product ecosystems deliver convenience and delight at every touchpoint.
Airbnb: Airbnb’s design promotes a feeling of adventure and belonging. Their software is also intuitive, accompanied by emotionally resonant imagery and personalized recommendations that make users feel valued travelers rather than customers.
Duolingo: The language learning app combines playful animations, gamification, and positive messages in learning. Duolingo convinces users that a difficult task is fun rather than the reverse.
Principles of Emotional Design
There are some key principles to implementing emotional design to get user engagement right. One is overwhelming empathy, as you must understand the user’s needs, preferences, and the points where they struggle most to create solutions that make the most sense personally. Equally, aesthetics are important because visually appealing designs can generate positive emotions and make you leave a strong first impression.
Consistency is the key to ensuring your brand experience is consistent; the brand experiences for all the touch points build trust and familiarity with your brand. The interactive elements help add value by incorporating playfulness and intrigue into the user's engagement. Personalization lets users feel valued and understood, enabling you to personalize the user's experience. Combining these principles forms a robust and powerful framework around emotional design.
Best Practices for Implementing Emotional Design
To apply emotional design for effect, UX and UI designers must take a user-centric approach based on strategy and empathy. The only thing that matters is to reach the audience, and you need to put in ample work to understand them and conduct research to know what emotional triggers or preferences would work for them. There are also tactics like leveraging color psychology since colors can make people feel certain things. For example, we could pick blue to invoke trust or yellow for optimism.
Playful animations and congratulatory messages that embed micro-interactions like these help break up the flow and make the experience a bit merrier. Storytelling also matters, allowing brands to link their stories with their owners’ stories, values, and dreams of belonging.
Conclusion
Emotional design is an excellent means to tune purchaser engagement, brand loyalty, and customer retention. Brands can lead a visceral, behavioral, or reflective experience with user emotional needs that resonate profoundly and leave an impression. We know from companies like Apple and Airbnb that emotional design is an investment in boosting user satisfaction that pays off over the long term.
Emotional design is a way to make yourself seen and connected with the user on a human level in a world of fierce competition. Businesses can build digital experiences that arouse and retain their audiences by prioritizing empathy, aesthetics, and personalization.

FAQs
Q: What is emotional design, and why is it important in user experience?
A: Emotional design aims to create more positive digital products, increasing users' emotional appeal and satisfaction with their usage.
Q: How does emotional design influence user engagement?
A: Emotional design improves trust, promotes exploration, and enhances memories of your experiences to improve user engagement.
Q: What are the key principles of emotional design?
A: The most crucial emotional design principles are empathy, aesthetics, consistency, interactivity, and personalization.
Q: Can emotional design improve customer retention?
A: Emotional design enables us to create positive emotional connections that help increase user loyalty and retention.
Q: How does color psychology contribute to emotional design?
A: Specific colors invoke specific emotions, which affect how users perceive and interact with that product. For instance, blue represents trust, and red represents excitement.
Emotional design goes beyond aesthetics and makes digital products valuable and meaningful to users. It achieves this by exploiting human emotions to make ordinary interactions extraordinary experiences, leading to increased engagement and loyalty. This approach is about creating interfaces that are not only pretty to look at but also make us feel safe, that we can trust, and that they’re exciting. Let’s explore how emotional design fuels engagement and how brands get noticed in this day and age of user-driven design.
The Role of Emotional Design in Building Meaningful User Experiences
Emotional design is creating digital products and experiences that connect emotionally with users. It goes beyond functionality to discover connections that make users feel understood, valued, and engaged. Emotional design makes interactions emotional with visual aesthetics, interactive elements, and psychology. Consequently, it plays a vital role in user experience (UX) as it closes the gap between user expectations and brand identity, and all interactions should feel intuitive and enjoyable.
Products that trigger emotions—such as joy, surprise, or trust—involve users and make it possible to engrave products in memory. Emotional design is a means to ensure that a user uses a product and not just the product, enabling him to stick to it and thus increase his probability of coming back. Not only would this increase usability, but it would also increase user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Connection Between Emotions and User Perception
How people feel about products is critical to interacting with and perceiving them. What users think when seeing a good app or website is often dictated by the emotional responses they get. A positive set of emotions distinguishes a good interface with the advantage of teaching users how to use it without much effort. On the other hand, a poorly designed interface can cause frustration in users, which will make them decide to abandon the product.
Cognitive psychology reveals that emotions drive decision-making. Users trust products that make them feel good, even if they do not feel good. Strategically fusing emotional design allows brands to influence users' behavior and perceptions to make their products a more attractive choice in the market.
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Don Norman, a pioneer in UX design, identified three levels of emotional design that contribute to the user experience: Behavioral, visceral, and reflective.

Visceral Design
This level of design is concerned with the product’s appearance and how it affects the user's first reaction. Items like color, typography, and layout create an immediate emotional reaction. For one, Apple's sleek product designs, which create a feeling of luxury and sophistication, help set a positive tone early on in the user experience.
Behavioral Design
The functionality and usability of a product are what behavioral design focuses on. I create a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when users become accustomed to an interface so seamlessly. Behavioral design — making booking a process other than checkout — is what brands like Airbnb have mastered.
Reflective Design
Thus, reflective design relates to how users understand their experience with the product they have used. The memory and cultural setting are just a tiny part of it, influenced by personal values. Take, for example, Nike's "Just Do It" campaigns, which resonate on a self-reflective level, encourage users, and help align with what the users wish to achieve.
Emotional design attains holistic and meaningful user experiences by engaging it at all three levels.
Why Emotional Design Is Critical for User Engagement
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, organization often refers to emotional design. Strong products that evoke strong emotional connections will stand out and lead users to engage with and advocate for the brand. Effective emotional design builds trust, promotes discovery, connects, and provides a sense of belonging, which is necessary for sustained engagement.
Additionally, emotional design plays into the basic human desire to connect. Emotional design allows brands to achieve this through interactive messages, empathetic messaging, and even personalized interactions through playful animations. Emotional resonance translates to higher retention rates and greater brand loyalty because products that provoke emotions have more likelihood of users coming back.
Emotions and Their Influence on Decision-Making and Loyalty
Decision-making is centered on emotions. According to neuroscience studies, when users decide to interact with a product, emotional responses usually trump rational thought. A good example is if you have a well-crafted onboarding process that promotes curiosity or fun, people will follow through, whereas a frustrating experience will make them abandon it.
Similar to emotions, emotions influence loyalty. Users are more likely to stay with a brand if they build a positive emotional connection to said brand. To make you feel understood and appreciated, companies like Spotify and Netflix have been excelling with emotional design to provide personal experiences to users.
Examples of Brands Successfully Leveraging Emotional Design
Notable brands such as Apple, Airbnb, and Duolingo have proven the power of emotional design in creating empathetic and memorable user experiences.
Apple: Apple’s minimalist design philosophy evokes elegance and exclusivity. The battlespace that Apple has engineered, starting with the iPhone and extending to the MacBook, is seamless, and its product ecosystems deliver convenience and delight at every touchpoint.
Airbnb: Airbnb’s design promotes a feeling of adventure and belonging. Their software is also intuitive, accompanied by emotionally resonant imagery and personalized recommendations that make users feel valued travelers rather than customers.
Duolingo: The language learning app combines playful animations, gamification, and positive messages in learning. Duolingo convinces users that a difficult task is fun rather than the reverse.
Principles of Emotional Design
There are some key principles to implementing emotional design to get user engagement right. One is overwhelming empathy, as you must understand the user’s needs, preferences, and the points where they struggle most to create solutions that make the most sense personally. Equally, aesthetics are important because visually appealing designs can generate positive emotions and make you leave a strong first impression.
Consistency is the key to ensuring your brand experience is consistent; the brand experiences for all the touch points build trust and familiarity with your brand. The interactive elements help add value by incorporating playfulness and intrigue into the user's engagement. Personalization lets users feel valued and understood, enabling you to personalize the user's experience. Combining these principles forms a robust and powerful framework around emotional design.
Best Practices for Implementing Emotional Design
To apply emotional design for effect, UX and UI designers must take a user-centric approach based on strategy and empathy. The only thing that matters is to reach the audience, and you need to put in ample work to understand them and conduct research to know what emotional triggers or preferences would work for them. There are also tactics like leveraging color psychology since colors can make people feel certain things. For example, we could pick blue to invoke trust or yellow for optimism.
Playful animations and congratulatory messages that embed micro-interactions like these help break up the flow and make the experience a bit merrier. Storytelling also matters, allowing brands to link their stories with their owners’ stories, values, and dreams of belonging.
Conclusion
Emotional design is an excellent means to tune purchaser engagement, brand loyalty, and customer retention. Brands can lead a visceral, behavioral, or reflective experience with user emotional needs that resonate profoundly and leave an impression. We know from companies like Apple and Airbnb that emotional design is an investment in boosting user satisfaction that pays off over the long term.
Emotional design is a way to make yourself seen and connected with the user on a human level in a world of fierce competition. Businesses can build digital experiences that arouse and retain their audiences by prioritizing empathy, aesthetics, and personalization.

FAQs
Q: What is emotional design, and why is it important in user experience?
A: Emotional design aims to create more positive digital products, increasing users' emotional appeal and satisfaction with their usage.
Q: How does emotional design influence user engagement?
A: Emotional design improves trust, promotes exploration, and enhances memories of your experiences to improve user engagement.
Q: What are the key principles of emotional design?
A: The most crucial emotional design principles are empathy, aesthetics, consistency, interactivity, and personalization.
Q: Can emotional design improve customer retention?
A: Emotional design enables us to create positive emotional connections that help increase user loyalty and retention.
Q: How does color psychology contribute to emotional design?
A: Specific colors invoke specific emotions, which affect how users perceive and interact with that product. For instance, blue represents trust, and red represents excitement.
Emotional design goes beyond aesthetics and makes digital products valuable and meaningful to users. It achieves this by exploiting human emotions to make ordinary interactions extraordinary experiences, leading to increased engagement and loyalty. This approach is about creating interfaces that are not only pretty to look at but also make us feel safe, that we can trust, and that they’re exciting. Let’s explore how emotional design fuels engagement and how brands get noticed in this day and age of user-driven design.
The Role of Emotional Design in Building Meaningful User Experiences
Emotional design is creating digital products and experiences that connect emotionally with users. It goes beyond functionality to discover connections that make users feel understood, valued, and engaged. Emotional design makes interactions emotional with visual aesthetics, interactive elements, and psychology. Consequently, it plays a vital role in user experience (UX) as it closes the gap between user expectations and brand identity, and all interactions should feel intuitive and enjoyable.
Products that trigger emotions—such as joy, surprise, or trust—involve users and make it possible to engrave products in memory. Emotional design is a means to ensure that a user uses a product and not just the product, enabling him to stick to it and thus increase his probability of coming back. Not only would this increase usability, but it would also increase user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Connection Between Emotions and User Perception
How people feel about products is critical to interacting with and perceiving them. What users think when seeing a good app or website is often dictated by the emotional responses they get. A positive set of emotions distinguishes a good interface with the advantage of teaching users how to use it without much effort. On the other hand, a poorly designed interface can cause frustration in users, which will make them decide to abandon the product.
Cognitive psychology reveals that emotions drive decision-making. Users trust products that make them feel good, even if they do not feel good. Strategically fusing emotional design allows brands to influence users' behavior and perceptions to make their products a more attractive choice in the market.
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Don Norman, a pioneer in UX design, identified three levels of emotional design that contribute to the user experience: Behavioral, visceral, and reflective.

Visceral Design
This level of design is concerned with the product’s appearance and how it affects the user's first reaction. Items like color, typography, and layout create an immediate emotional reaction. For one, Apple's sleek product designs, which create a feeling of luxury and sophistication, help set a positive tone early on in the user experience.
Behavioral Design
The functionality and usability of a product are what behavioral design focuses on. I create a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when users become accustomed to an interface so seamlessly. Behavioral design — making booking a process other than checkout — is what brands like Airbnb have mastered.
Reflective Design
Thus, reflective design relates to how users understand their experience with the product they have used. The memory and cultural setting are just a tiny part of it, influenced by personal values. Take, for example, Nike's "Just Do It" campaigns, which resonate on a self-reflective level, encourage users, and help align with what the users wish to achieve.
Emotional design attains holistic and meaningful user experiences by engaging it at all three levels.
Why Emotional Design Is Critical for User Engagement
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, organization often refers to emotional design. Strong products that evoke strong emotional connections will stand out and lead users to engage with and advocate for the brand. Effective emotional design builds trust, promotes discovery, connects, and provides a sense of belonging, which is necessary for sustained engagement.
Additionally, emotional design plays into the basic human desire to connect. Emotional design allows brands to achieve this through interactive messages, empathetic messaging, and even personalized interactions through playful animations. Emotional resonance translates to higher retention rates and greater brand loyalty because products that provoke emotions have more likelihood of users coming back.
Emotions and Their Influence on Decision-Making and Loyalty
Decision-making is centered on emotions. According to neuroscience studies, when users decide to interact with a product, emotional responses usually trump rational thought. A good example is if you have a well-crafted onboarding process that promotes curiosity or fun, people will follow through, whereas a frustrating experience will make them abandon it.
Similar to emotions, emotions influence loyalty. Users are more likely to stay with a brand if they build a positive emotional connection to said brand. To make you feel understood and appreciated, companies like Spotify and Netflix have been excelling with emotional design to provide personal experiences to users.
Examples of Brands Successfully Leveraging Emotional Design
Notable brands such as Apple, Airbnb, and Duolingo have proven the power of emotional design in creating empathetic and memorable user experiences.
Apple: Apple’s minimalist design philosophy evokes elegance and exclusivity. The battlespace that Apple has engineered, starting with the iPhone and extending to the MacBook, is seamless, and its product ecosystems deliver convenience and delight at every touchpoint.
Airbnb: Airbnb’s design promotes a feeling of adventure and belonging. Their software is also intuitive, accompanied by emotionally resonant imagery and personalized recommendations that make users feel valued travelers rather than customers.
Duolingo: The language learning app combines playful animations, gamification, and positive messages in learning. Duolingo convinces users that a difficult task is fun rather than the reverse.
Principles of Emotional Design
There are some key principles to implementing emotional design to get user engagement right. One is overwhelming empathy, as you must understand the user’s needs, preferences, and the points where they struggle most to create solutions that make the most sense personally. Equally, aesthetics are important because visually appealing designs can generate positive emotions and make you leave a strong first impression.
Consistency is the key to ensuring your brand experience is consistent; the brand experiences for all the touch points build trust and familiarity with your brand. The interactive elements help add value by incorporating playfulness and intrigue into the user's engagement. Personalization lets users feel valued and understood, enabling you to personalize the user's experience. Combining these principles forms a robust and powerful framework around emotional design.
Best Practices for Implementing Emotional Design
To apply emotional design for effect, UX and UI designers must take a user-centric approach based on strategy and empathy. The only thing that matters is to reach the audience, and you need to put in ample work to understand them and conduct research to know what emotional triggers or preferences would work for them. There are also tactics like leveraging color psychology since colors can make people feel certain things. For example, we could pick blue to invoke trust or yellow for optimism.
Playful animations and congratulatory messages that embed micro-interactions like these help break up the flow and make the experience a bit merrier. Storytelling also matters, allowing brands to link their stories with their owners’ stories, values, and dreams of belonging.
Conclusion
Emotional design is an excellent means to tune purchaser engagement, brand loyalty, and customer retention. Brands can lead a visceral, behavioral, or reflective experience with user emotional needs that resonate profoundly and leave an impression. We know from companies like Apple and Airbnb that emotional design is an investment in boosting user satisfaction that pays off over the long term.
Emotional design is a way to make yourself seen and connected with the user on a human level in a world of fierce competition. Businesses can build digital experiences that arouse and retain their audiences by prioritizing empathy, aesthetics, and personalization.

FAQs
Q: What is emotional design, and why is it important in user experience?
A: Emotional design aims to create more positive digital products, increasing users' emotional appeal and satisfaction with their usage.
Q: How does emotional design influence user engagement?
A: Emotional design improves trust, promotes exploration, and enhances memories of your experiences to improve user engagement.
Q: What are the key principles of emotional design?
A: The most crucial emotional design principles are empathy, aesthetics, consistency, interactivity, and personalization.
Q: Can emotional design improve customer retention?
A: Emotional design enables us to create positive emotional connections that help increase user loyalty and retention.
Q: How does color psychology contribute to emotional design?
A: Specific colors invoke specific emotions, which affect how users perceive and interact with that product. For instance, blue represents trust, and red represents excitement.
Emotional design goes beyond aesthetics and makes digital products valuable and meaningful to users. It achieves this by exploiting human emotions to make ordinary interactions extraordinary experiences, leading to increased engagement and loyalty. This approach is about creating interfaces that are not only pretty to look at but also make us feel safe, that we can trust, and that they’re exciting. Let’s explore how emotional design fuels engagement and how brands get noticed in this day and age of user-driven design.
The Role of Emotional Design in Building Meaningful User Experiences
Emotional design is creating digital products and experiences that connect emotionally with users. It goes beyond functionality to discover connections that make users feel understood, valued, and engaged. Emotional design makes interactions emotional with visual aesthetics, interactive elements, and psychology. Consequently, it plays a vital role in user experience (UX) as it closes the gap between user expectations and brand identity, and all interactions should feel intuitive and enjoyable.
Products that trigger emotions—such as joy, surprise, or trust—involve users and make it possible to engrave products in memory. Emotional design is a means to ensure that a user uses a product and not just the product, enabling him to stick to it and thus increase his probability of coming back. Not only would this increase usability, but it would also increase user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Connection Between Emotions and User Perception
How people feel about products is critical to interacting with and perceiving them. What users think when seeing a good app or website is often dictated by the emotional responses they get. A positive set of emotions distinguishes a good interface with the advantage of teaching users how to use it without much effort. On the other hand, a poorly designed interface can cause frustration in users, which will make them decide to abandon the product.
Cognitive psychology reveals that emotions drive decision-making. Users trust products that make them feel good, even if they do not feel good. Strategically fusing emotional design allows brands to influence users' behavior and perceptions to make their products a more attractive choice in the market.
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Don Norman, a pioneer in UX design, identified three levels of emotional design that contribute to the user experience: Behavioral, visceral, and reflective.

Visceral Design
This level of design is concerned with the product’s appearance and how it affects the user's first reaction. Items like color, typography, and layout create an immediate emotional reaction. For one, Apple's sleek product designs, which create a feeling of luxury and sophistication, help set a positive tone early on in the user experience.
Behavioral Design
The functionality and usability of a product are what behavioral design focuses on. I create a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when users become accustomed to an interface so seamlessly. Behavioral design — making booking a process other than checkout — is what brands like Airbnb have mastered.
Reflective Design
Thus, reflective design relates to how users understand their experience with the product they have used. The memory and cultural setting are just a tiny part of it, influenced by personal values. Take, for example, Nike's "Just Do It" campaigns, which resonate on a self-reflective level, encourage users, and help align with what the users wish to achieve.
Emotional design attains holistic and meaningful user experiences by engaging it at all three levels.
Why Emotional Design Is Critical for User Engagement
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, organization often refers to emotional design. Strong products that evoke strong emotional connections will stand out and lead users to engage with and advocate for the brand. Effective emotional design builds trust, promotes discovery, connects, and provides a sense of belonging, which is necessary for sustained engagement.
Additionally, emotional design plays into the basic human desire to connect. Emotional design allows brands to achieve this through interactive messages, empathetic messaging, and even personalized interactions through playful animations. Emotional resonance translates to higher retention rates and greater brand loyalty because products that provoke emotions have more likelihood of users coming back.
Emotions and Their Influence on Decision-Making and Loyalty
Decision-making is centered on emotions. According to neuroscience studies, when users decide to interact with a product, emotional responses usually trump rational thought. A good example is if you have a well-crafted onboarding process that promotes curiosity or fun, people will follow through, whereas a frustrating experience will make them abandon it.
Similar to emotions, emotions influence loyalty. Users are more likely to stay with a brand if they build a positive emotional connection to said brand. To make you feel understood and appreciated, companies like Spotify and Netflix have been excelling with emotional design to provide personal experiences to users.
Examples of Brands Successfully Leveraging Emotional Design
Notable brands such as Apple, Airbnb, and Duolingo have proven the power of emotional design in creating empathetic and memorable user experiences.
Apple: Apple’s minimalist design philosophy evokes elegance and exclusivity. The battlespace that Apple has engineered, starting with the iPhone and extending to the MacBook, is seamless, and its product ecosystems deliver convenience and delight at every touchpoint.
Airbnb: Airbnb’s design promotes a feeling of adventure and belonging. Their software is also intuitive, accompanied by emotionally resonant imagery and personalized recommendations that make users feel valued travelers rather than customers.
Duolingo: The language learning app combines playful animations, gamification, and positive messages in learning. Duolingo convinces users that a difficult task is fun rather than the reverse.
Principles of Emotional Design
There are some key principles to implementing emotional design to get user engagement right. One is overwhelming empathy, as you must understand the user’s needs, preferences, and the points where they struggle most to create solutions that make the most sense personally. Equally, aesthetics are important because visually appealing designs can generate positive emotions and make you leave a strong first impression.
Consistency is the key to ensuring your brand experience is consistent; the brand experiences for all the touch points build trust and familiarity with your brand. The interactive elements help add value by incorporating playfulness and intrigue into the user's engagement. Personalization lets users feel valued and understood, enabling you to personalize the user's experience. Combining these principles forms a robust and powerful framework around emotional design.
Best Practices for Implementing Emotional Design
To apply emotional design for effect, UX and UI designers must take a user-centric approach based on strategy and empathy. The only thing that matters is to reach the audience, and you need to put in ample work to understand them and conduct research to know what emotional triggers or preferences would work for them. There are also tactics like leveraging color psychology since colors can make people feel certain things. For example, we could pick blue to invoke trust or yellow for optimism.
Playful animations and congratulatory messages that embed micro-interactions like these help break up the flow and make the experience a bit merrier. Storytelling also matters, allowing brands to link their stories with their owners’ stories, values, and dreams of belonging.
Conclusion
Emotional design is an excellent means to tune purchaser engagement, brand loyalty, and customer retention. Brands can lead a visceral, behavioral, or reflective experience with user emotional needs that resonate profoundly and leave an impression. We know from companies like Apple and Airbnb that emotional design is an investment in boosting user satisfaction that pays off over the long term.
Emotional design is a way to make yourself seen and connected with the user on a human level in a world of fierce competition. Businesses can build digital experiences that arouse and retain their audiences by prioritizing empathy, aesthetics, and personalization.

FAQs
Q: What is emotional design, and why is it important in user experience?
A: Emotional design aims to create more positive digital products, increasing users' emotional appeal and satisfaction with their usage.
Q: How does emotional design influence user engagement?
A: Emotional design improves trust, promotes exploration, and enhances memories of your experiences to improve user engagement.
Q: What are the key principles of emotional design?
A: The most crucial emotional design principles are empathy, aesthetics, consistency, interactivity, and personalization.
Q: Can emotional design improve customer retention?
A: Emotional design enables us to create positive emotional connections that help increase user loyalty and retention.
Q: How does color psychology contribute to emotional design?
A: Specific colors invoke specific emotions, which affect how users perceive and interact with that product. For instance, blue represents trust, and red represents excitement.
Emotional design goes beyond aesthetics and makes digital products valuable and meaningful to users. It achieves this by exploiting human emotions to make ordinary interactions extraordinary experiences, leading to increased engagement and loyalty. This approach is about creating interfaces that are not only pretty to look at but also make us feel safe, that we can trust, and that they’re exciting. Let’s explore how emotional design fuels engagement and how brands get noticed in this day and age of user-driven design.
The Role of Emotional Design in Building Meaningful User Experiences
Emotional design is creating digital products and experiences that connect emotionally with users. It goes beyond functionality to discover connections that make users feel understood, valued, and engaged. Emotional design makes interactions emotional with visual aesthetics, interactive elements, and psychology. Consequently, it plays a vital role in user experience (UX) as it closes the gap between user expectations and brand identity, and all interactions should feel intuitive and enjoyable.
Products that trigger emotions—such as joy, surprise, or trust—involve users and make it possible to engrave products in memory. Emotional design is a means to ensure that a user uses a product and not just the product, enabling him to stick to it and thus increase his probability of coming back. Not only would this increase usability, but it would also increase user satisfaction and brand loyalty.
The Connection Between Emotions and User Perception
How people feel about products is critical to interacting with and perceiving them. What users think when seeing a good app or website is often dictated by the emotional responses they get. A positive set of emotions distinguishes a good interface with the advantage of teaching users how to use it without much effort. On the other hand, a poorly designed interface can cause frustration in users, which will make them decide to abandon the product.
Cognitive psychology reveals that emotions drive decision-making. Users trust products that make them feel good, even if they do not feel good. Strategically fusing emotional design allows brands to influence users' behavior and perceptions to make their products a more attractive choice in the market.
The Three Levels of Emotional Design
Don Norman, a pioneer in UX design, identified three levels of emotional design that contribute to the user experience: Behavioral, visceral, and reflective.

Visceral Design
This level of design is concerned with the product’s appearance and how it affects the user's first reaction. Items like color, typography, and layout create an immediate emotional reaction. For one, Apple's sleek product designs, which create a feeling of luxury and sophistication, help set a positive tone early on in the user experience.
Behavioral Design
The functionality and usability of a product are what behavioral design focuses on. I create a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction when users become accustomed to an interface so seamlessly. Behavioral design — making booking a process other than checkout — is what brands like Airbnb have mastered.
Reflective Design
Thus, reflective design relates to how users understand their experience with the product they have used. The memory and cultural setting are just a tiny part of it, influenced by personal values. Take, for example, Nike's "Just Do It" campaigns, which resonate on a self-reflective level, encourage users, and help align with what the users wish to achieve.
Emotional design attains holistic and meaningful user experiences by engaging it at all three levels.
Why Emotional Design Is Critical for User Engagement
In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, organization often refers to emotional design. Strong products that evoke strong emotional connections will stand out and lead users to engage with and advocate for the brand. Effective emotional design builds trust, promotes discovery, connects, and provides a sense of belonging, which is necessary for sustained engagement.
Additionally, emotional design plays into the basic human desire to connect. Emotional design allows brands to achieve this through interactive messages, empathetic messaging, and even personalized interactions through playful animations. Emotional resonance translates to higher retention rates and greater brand loyalty because products that provoke emotions have more likelihood of users coming back.
Emotions and Their Influence on Decision-Making and Loyalty
Decision-making is centered on emotions. According to neuroscience studies, when users decide to interact with a product, emotional responses usually trump rational thought. A good example is if you have a well-crafted onboarding process that promotes curiosity or fun, people will follow through, whereas a frustrating experience will make them abandon it.
Similar to emotions, emotions influence loyalty. Users are more likely to stay with a brand if they build a positive emotional connection to said brand. To make you feel understood and appreciated, companies like Spotify and Netflix have been excelling with emotional design to provide personal experiences to users.
Examples of Brands Successfully Leveraging Emotional Design
Notable brands such as Apple, Airbnb, and Duolingo have proven the power of emotional design in creating empathetic and memorable user experiences.
Apple: Apple’s minimalist design philosophy evokes elegance and exclusivity. The battlespace that Apple has engineered, starting with the iPhone and extending to the MacBook, is seamless, and its product ecosystems deliver convenience and delight at every touchpoint.
Airbnb: Airbnb’s design promotes a feeling of adventure and belonging. Their software is also intuitive, accompanied by emotionally resonant imagery and personalized recommendations that make users feel valued travelers rather than customers.
Duolingo: The language learning app combines playful animations, gamification, and positive messages in learning. Duolingo convinces users that a difficult task is fun rather than the reverse.
Principles of Emotional Design
There are some key principles to implementing emotional design to get user engagement right. One is overwhelming empathy, as you must understand the user’s needs, preferences, and the points where they struggle most to create solutions that make the most sense personally. Equally, aesthetics are important because visually appealing designs can generate positive emotions and make you leave a strong first impression.
Consistency is the key to ensuring your brand experience is consistent; the brand experiences for all the touch points build trust and familiarity with your brand. The interactive elements help add value by incorporating playfulness and intrigue into the user's engagement. Personalization lets users feel valued and understood, enabling you to personalize the user's experience. Combining these principles forms a robust and powerful framework around emotional design.
Best Practices for Implementing Emotional Design
To apply emotional design for effect, UX and UI designers must take a user-centric approach based on strategy and empathy. The only thing that matters is to reach the audience, and you need to put in ample work to understand them and conduct research to know what emotional triggers or preferences would work for them. There are also tactics like leveraging color psychology since colors can make people feel certain things. For example, we could pick blue to invoke trust or yellow for optimism.
Playful animations and congratulatory messages that embed micro-interactions like these help break up the flow and make the experience a bit merrier. Storytelling also matters, allowing brands to link their stories with their owners’ stories, values, and dreams of belonging.
Conclusion
Emotional design is an excellent means to tune purchaser engagement, brand loyalty, and customer retention. Brands can lead a visceral, behavioral, or reflective experience with user emotional needs that resonate profoundly and leave an impression. We know from companies like Apple and Airbnb that emotional design is an investment in boosting user satisfaction that pays off over the long term.
Emotional design is a way to make yourself seen and connected with the user on a human level in a world of fierce competition. Businesses can build digital experiences that arouse and retain their audiences by prioritizing empathy, aesthetics, and personalization.

FAQs
Q: What is emotional design, and why is it important in user experience?
A: Emotional design aims to create more positive digital products, increasing users' emotional appeal and satisfaction with their usage.
Q: How does emotional design influence user engagement?
A: Emotional design improves trust, promotes exploration, and enhances memories of your experiences to improve user engagement.
Q: What are the key principles of emotional design?
A: The most crucial emotional design principles are empathy, aesthetics, consistency, interactivity, and personalization.
Q: Can emotional design improve customer retention?
A: Emotional design enables us to create positive emotional connections that help increase user loyalty and retention.
Q: How does color psychology contribute to emotional design?
A: Specific colors invoke specific emotions, which affect how users perceive and interact with that product. For instance, blue represents trust, and red represents excitement.
Recent Posts
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India






